Sodium sulfate (Na₂SO₄) is a common component in industrial wastewaters, particularly from flue gas desulfurization (FGD) plants. To meet increasingly strict discharge regulations, sodium sulfate is often removed by crystallization and, in many cases, recovered as a valuable product. The same separation challenge is well known in industries such as viscose fiber production.
Depending on process conditions, sodium sulfate can be crystallized either as an anhydrous salt using evaporation crystallization above the transformation temperature or as sodium sulfate decahydrate (Glauber’s salt) via cooling crystallization below approximately 32 °C. For evaporation crystallization, energy-efficient mechanical vapor recompression (MVR) is commonly applied, while cooling crystallization offers the advantage of reducing both salt load and wastewater volume.
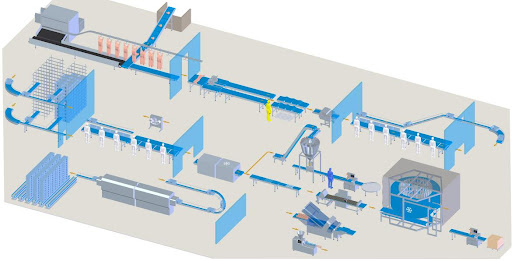
After crystallization, centrifuges are used for efficient solid–liquid separation, producing wet sodium sulfate crystals that require reliable downstream handling.
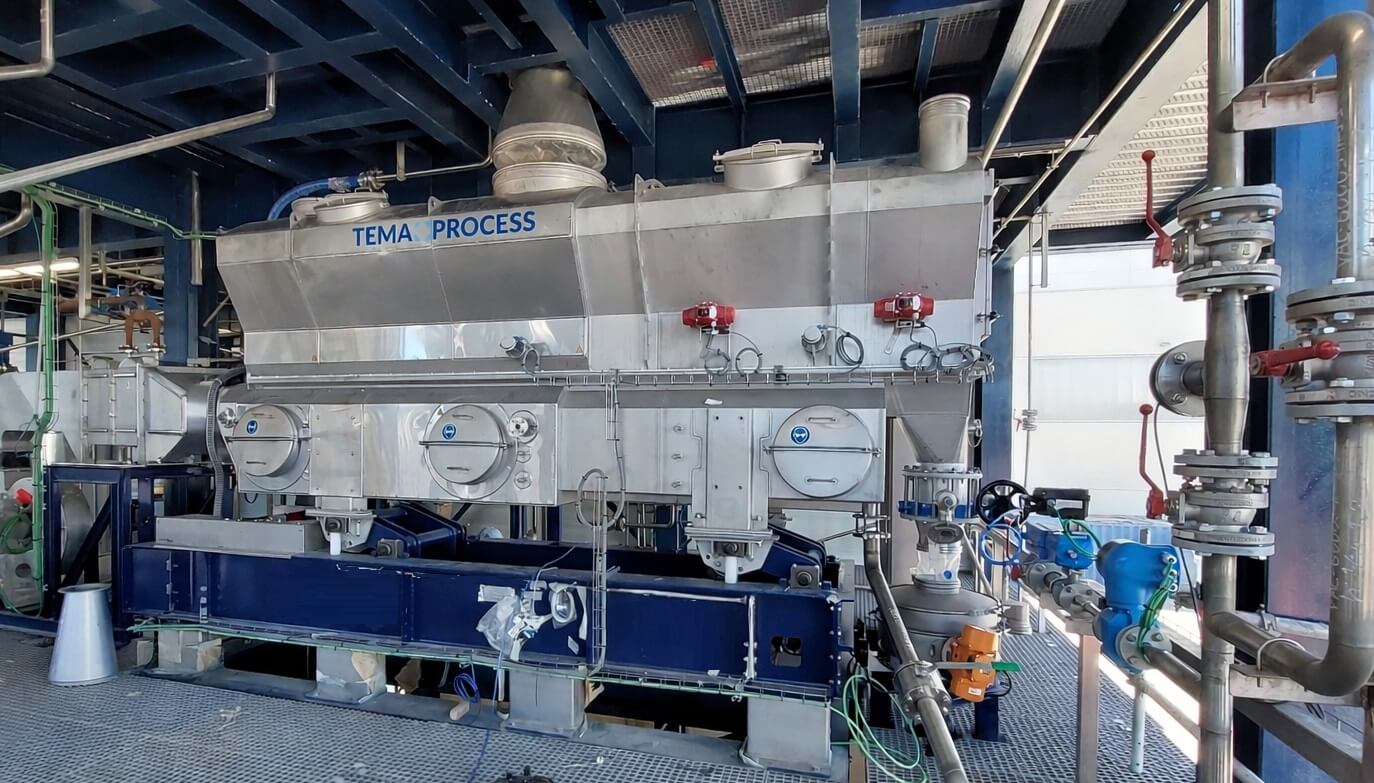
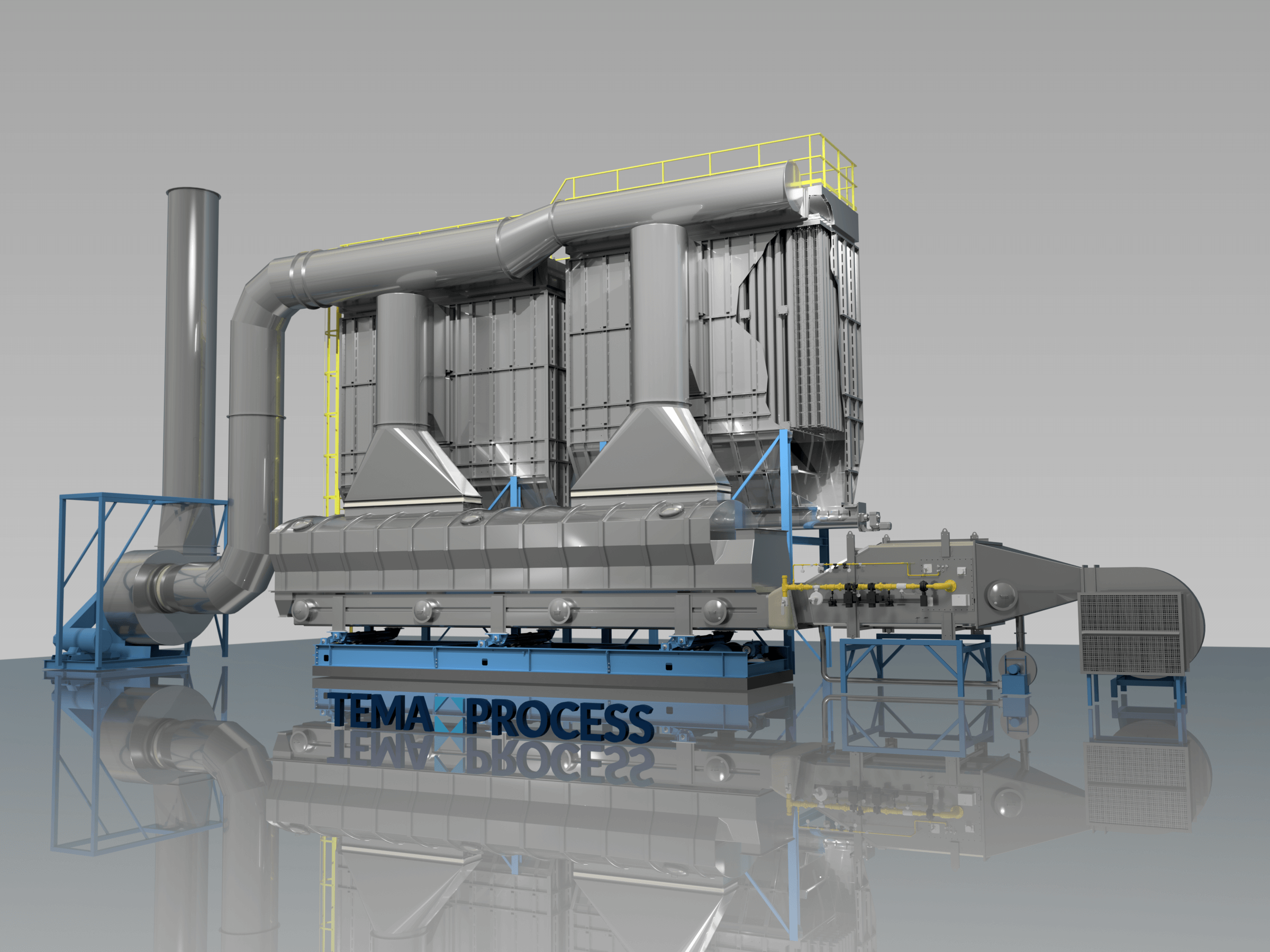
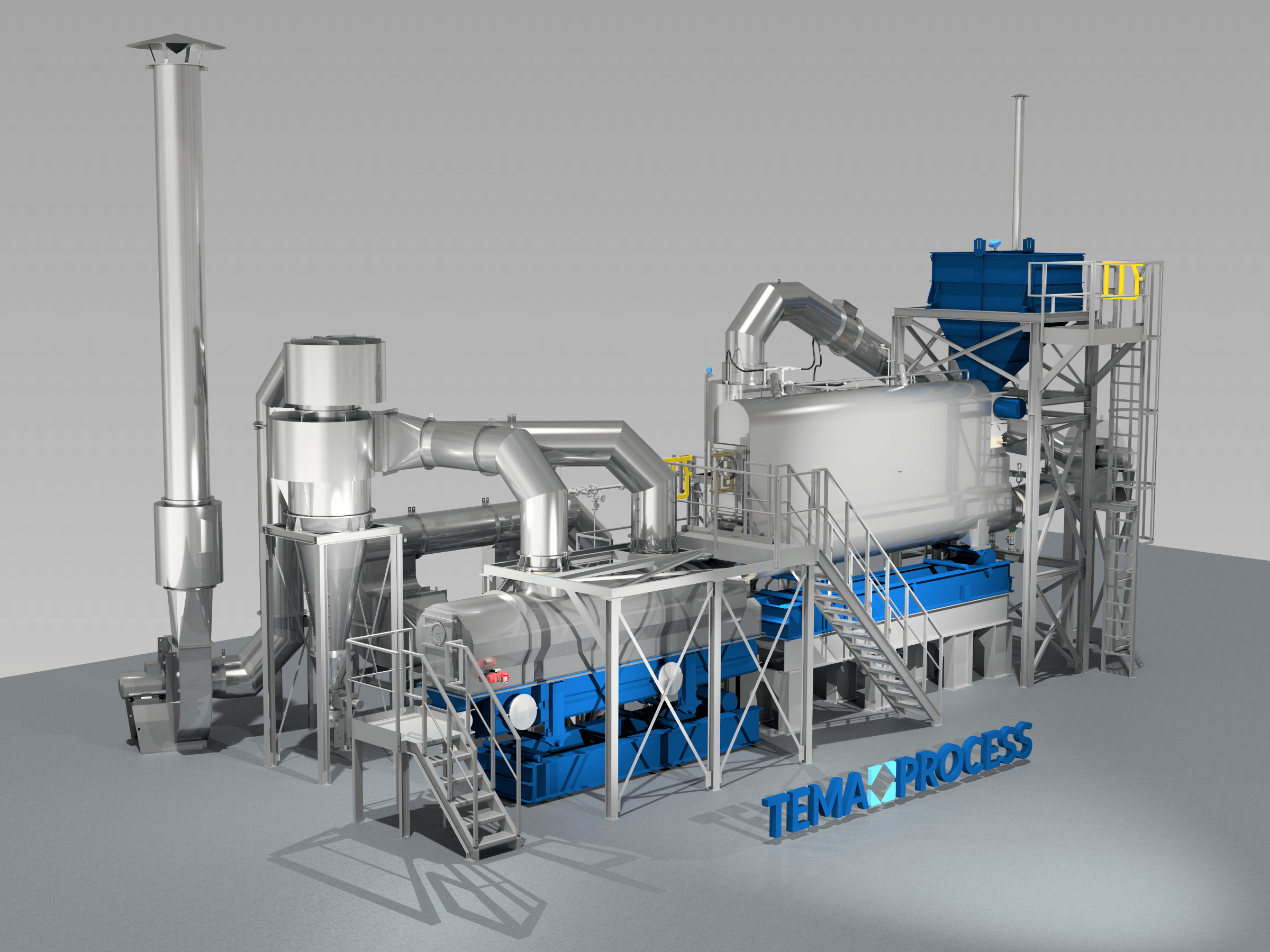
TEMA Process specializes in the drying and cooling of crystalline products.
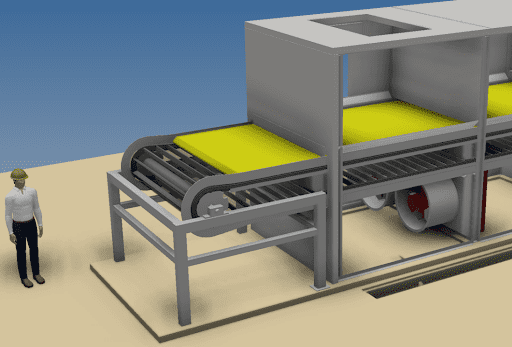
Using robust fluid bed drying and cooling technology, TEMA Process converts wet sodium sulfate crystals into a free-flowing, stable product with precisely controlled residual moisture. Drying and cooling are combined in one compact system, ensuring gentle product treatment, consistent quality, and reliable operation.
By focusing on the critical downstream steps after crystallization, TEMA Process enables safe handling, storage, transport, and reuse of sodium sulfate, supporting both regulatory compliance and sustainable resource recovery.
#SodiumSulfate
#IndustrialWastewater
#FGD
#Crystallization
#SolidLiquidSeparation
#FluidBedDryer
#ProcessEngineering
#SustainableIndustry
#ResourceRecovery
#TemaProcess